Sheet Metal and Heavy Plates Flattening and Parts Leveling Machine (1.5 mm to 8 mm)
In modern manufacturing, especially in industries such as automotive, aerospace, metal fabrication, and heavy machinery, precision and flatness are key to ensuring the quality and performance of metal parts. Sheet metal and heavy plates that have been processed through methods such as laser cutting, plasma cutting, and punching often suffer from distortions like warps, bends, or residual stresses. These distortions need to be corrected before the parts can undergo further processing, welding, or assembly. This is where sheet metal flattening and parts leveling machines come into play.
This article introduces sheet metal and heavy plates flattening and parts leveling machines designed to handle materials with thicknesses ranging from 1.5 mm to 8.0 mm. These machines are capable of leveling a wide variety of materials, including laser-cut, plasma-cut, punched parts, sheets, and heavy plates. The machines come with passage widths available from 400 mm to 2200 mm, making them versatile enough to handle a range of sizes and applications.
What are Sheet Metal and Heavy Plate Leveling Machines?
A sheet metal and heavy plates leveling machine is a device used to flatten or straighten metal parts that have been deformed during manufacturing processes like laser cutting, plasma cutting, and punching. These processes introduce thermal stresses, warps, and other distortions into the material, which can affect its performance, appearance, and further processing.
Leveling machines are designed with a series of rollers arranged in a specific pattern to apply controlled pressure to the sheet or plate, gradually bending the material in the opposite direction to correct these distortions. The result is a perfectly flat sheet or plate with minimal residual stress, which is essential for parts that will undergo additional manufacturing or assembly processes.
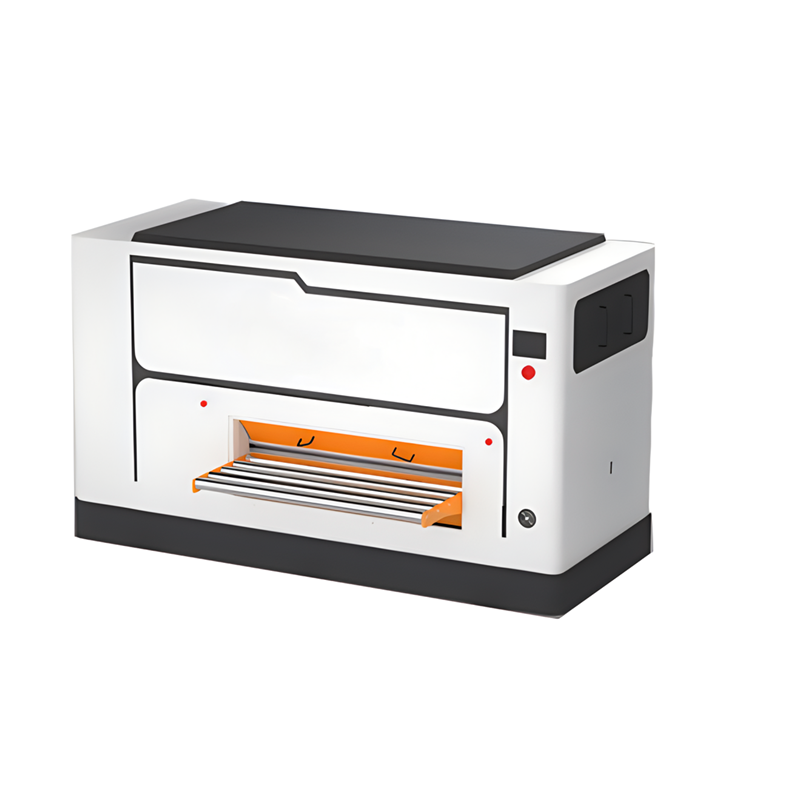

Key Features and Specifications
1. Material Thickness Range: 1.5 mm to 8.0 mm
These leveling machines are ideal for handling materials with thicknesses ranging from 1.5 mm to 8.0 mm. This broad thickness range allows the machines to work with both thin metal sheets and thicker, heavier plates. The versatility in thickness makes these machines suitable for a variety of industries and applications.
For thin sheets (1.5 mm to 3.0 mm), the machine applies light bending forces to achieve flatness, while for thicker plates (4.0 mm to 8.0 mm), the machine uses higher force and more robust roller systems to correct the deformations effectively. This flexibility is essential in industries where different thicknesses of sheet metal or plates are used for various components.
2. Passage Widths Available: 400 mm to 2200 mm
The leveling machines are available with a variety of passage widths to accommodate different sizes of metal parts. The widths available range from 400 mm to 2200 mm, ensuring that the machine can handle both small and large parts efficiently. The wider passage widths allow for the processing of larger sheets or plates, which are common in heavy machinery, construction, and automotive applications.
For small parts, narrower passage widths (e.g., 400 mm, 600 mm, or 800 mm) are ideal, while for larger parts or heavy plates, the wider passage widths (e.g., 1800 mm, 2000 mm, or 2200 mm) provide the necessary space for leveling large components. This range of passage widths ensures the machine can handle a wide variety of material sizes, making it a versatile tool for metalworking shops and industrial manufacturers.
3. Materials Processed
The sheet metal and heavy plates leveling machine is designed to work with a wide range of materials, including:
Laser Cut Parts: Laser cutting produces clean edges but may cause warping due to the heat involved. A leveling machine straightens these parts by removing any thermal deformations, ensuring a flat, precise surface.
Plasma Cut Parts: Plasma cutting often results in rough edges and potential warping due to the heat of the plasma arc. The leveling machine can eliminate these distortions, ensuring that the plasma cut parts are ready for welding, coating, or further processing.
Punched Parts: Punched parts can suffer from edge distortions and residual stresses. The leveling machine effectively straightens these parts to ensure they fit properly in their final application.
Sheets and Plates: The machine is ideal for processing both thin and thick sheets and plates, making it suitable for applications in heavy fabrication, construction, and metalworking industries.
4. Roller System for Flatness Control
The core function of the leveling machine is its roller system, which applies controlled pressure to the metal sheet or plate. The rollers are arranged in a specific configuration, with the upper and lower rollers applying opposing forces to bend the material in the opposite direction of the deformation.
The roller gap can be adjusted based on the material thickness, allowing for precise control over the leveling process. For thinner sheets, the gap is set narrow to apply light pressure, while for thicker plates, the gap is widened to apply greater force. The machine’s rollers work together to gradually flatten the material while maintaining its structural integrity.
5. Adjustable Pressure and Gap Control
To ensure optimal leveling results, the machine includes an adjustable pressure control system. The pressure applied by the rollers is automatically adjusted based on the material thickness and type, ensuring that the correct amount of force is used for each part.
The gap control feature enables precise adjustments for different material thicknesses, from 1.5 mm to 8.0 mm. By continuously monitoring and adjusting the roller gap and pressure, the machine ensures consistent and uniform flattening, resulting in high-quality, flat metal parts.
6. Speed and Efficiency
These leveling machines are designed to operate at variable speeds, allowing manufacturers to optimize throughput based on the material type and thickness. The speed of operation can range from 0 to 12 meters per minute, with faster speeds generally used for thinner materials and slower speeds for thicker plates. This flexibility allows manufacturers to balance processing speed with the need for high precision.
For high-volume applications, the machine can operate at high speeds while maintaining accuracy and ensuring consistent flatness across a large batch of parts.
7. Robust Build and Durability
The leveling machines are built to withstand the rigorous demands of industrial metalworking environments. They feature heavy-duty construction, with strong frames and durable rollers designed to handle large, heavy plates and thick materials. The robust design ensures long-term reliability and minimal maintenance, even under heavy usage.
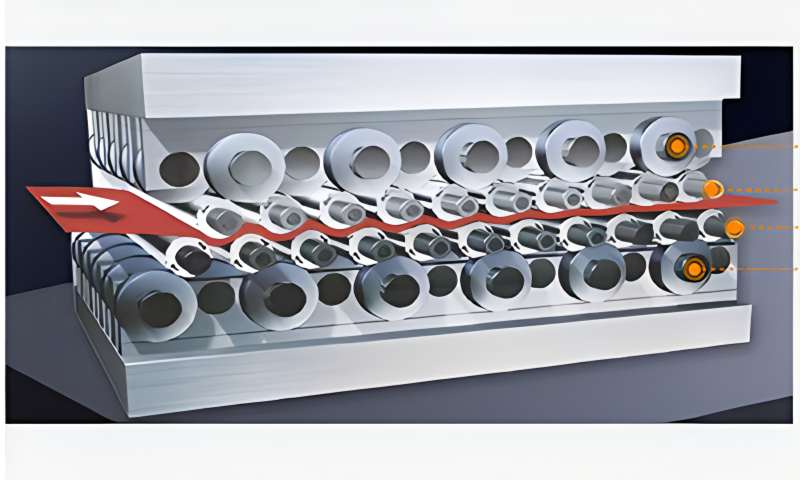
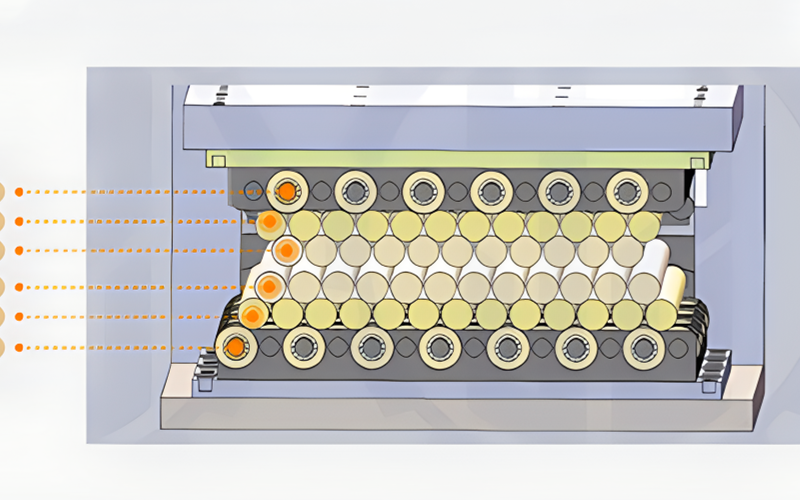
How the Leveling Machine Works
The process of flattening and leveling sheet metal and heavy plates involves several stages:
Material Entry
The metal sheet or plate is fed into the machine through the entry rollers. These rollers ensure that the material is properly aligned before it enters the main leveling area.
Roller Flattening
Once the material is in position, it passes through a series of upper and lower rollers. These rollers apply opposing forces to the sheet or plate, gradually bending it in the opposite direction of its deformations. The material moves through the rollers in a progressive flattening process, with the level of force applied depending on the thickness of the material.
Gap and Pressure Adjustment
The machine’s control system continuously adjusts the gap between the rollers and the pressure applied to the material. This ensures that the correct force is applied at all stages of the leveling process. For thicker materials, higher pressure is used to achieve a flatter surface, while for thinner materials, lighter pressure is applied to prevent over-straightening.
Material Exit and Quality Check
After passing through the rollers, the leveled sheet or plate exits the machine. Some leveling machines are equipped with flatness measurement systems to verify the accuracy of the leveling process. In some cases, the material may undergo an additional inspection to ensure that it meets the required flatness specifications.
Final Product
The leveled metal parts, sheets, or plates are now ready for further processing, including welding, coating, or assembly, depending on the application. The consistent flatness achieved by the leveling machine ensures that these parts fit precisely and perform reliably in their intended application.
Applications and Industries
The sheet metal and heavy plates leveling machine is an essential tool in various industries that require high-precision metal parts. Some of the key industries and applications include:
Automotive Manufacturing: To produce flat metal components, body panels, and chassis parts, ensuring smooth assembly and fitment.
Aerospace: For leveling critical structural components and parts that require precise flatness for safety and performance.
Heavy Equipment Manufacturing: To level large, thick plates used in the production of industrial machines, vehicles, and structural components.
Metal Fabrication: For processing laser cut, plasma cut, and punched metal parts that need to be perfectly flat for further fabrication processes.
Construction: To prepare large steel plates and sheets for use in construction, ensuring that they fit together properly during assembly.





















